13 KiB
Introduction
A captive portal is a web page accessed with a web browser that is displayed to newly connected users of a Wi-Fi network before they are granted broader access to network resources.
To determinate if a captive portal has to be display and ask to passenger for an action, a device (personnal computer, phone or tablet of both Android and iOS) calls some APIs. When this API sends:
- 204 HTTP Code: device has connectivity nothing to do.
- 302 HTTP Code: device may have connectivity but passenger has to signin.
- No answer: device don't have connectivity but device doesn't known what to do
The goal of PXPortal is to simulate captive portal APIs from different constructors by answering required HTTP codes.
WARNING
The behavior describes here is based on experimentation as devices do not properly disclose their logic. As each phone constructor implements its own API or internal mechanism, this solution may not work on all phones (for example the behavior of last Samsung release is different). The list of captive API will be updated over time.
PXPortal
PXPortal is composed of three services:
- dnsmasq: provides Domain Name System (DNS) forwarder, Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server, router advertisement and network boot features for small computer networks, created as free software
- portal_service: internal PXCom service to simuate captive portal API
- nginx: a web server which can also be used as a reverse proxy, load balancer, mail proxy and HTTP cache
participant Device
participant Box
participant Dnsmasq
participant Nginx
participant Portal_Service
Device -> Box: connectivitycheck.google.com
Box -> Dnsmasq: Whois google.com
Dnsmasq --> Box: server's IP
Box -> Nginx: connectivitycheck.google.com
Nginx -> Portal_Service: Is a validated mac address
alt Not Valid
Portal_Service --> Nginx: Code 302 - Redirect to http://[PortalPage]
else
Portal_Service --> Nginx: Code 204
end
Nginx --> Box: Portal_Service response
Box --> Device: Portal_Service response
To have a valid mac address, a passenger has to accept terms of use on portal webpage. On this action, a request is sent to portal_service which will save in memory the mac address as a valid one. Next time, passenger will be considered as a valid user and no new signin notification will be shown.
participant Device
participant Portal_Service
Device -> Portal_Service: http://captive.eca.aero/validate
Portal_Service -> Portal_Service: Flag MAC as valid
Portal_Service --> Device: OK
\clearpage
PXPortal - DNSmasq
- redirects all captive portal API to the box. With the following configuration, PXPortal can handles Android and iOS phones and some linux.
- (optional) can provide a DHCP server (not used here)
# ANDROID
address=/google.com/10.0.0.254
address=/.google.com/10.0.0.254
address=/gstatic.com/10.0.0.254
address=/.gstatic.com/10.0.0.254
address=/android.com/10.0.0.254
address=/.android.com/10.0.0.254
# IOS
address=/apple.com/10.0.0.254
address=/.apple.com/10.0.0.254
# BROWSER
address=/firefox.com/10.0.0.254
address=/.firefox.com/10.0.0.254
# LINUX
address=/ubuntu.com/10.0.0.254
address=/.ubuntu.com/10.0.0.254
address=/gnome.org/10.0.0.254
address=/.gnome.org/10.0.0.254
PXPortal - Nginx
- handles all requests sent to captive portal API and forwards them to our pxportal service,
- and serves portal webpages on http://portal.eca.aero/index.html and http://portal.eca.aero/ready.html
server {
server_name captive.eca.aero
*.apple.com
*.gstatic.com
*.firefox.com
*.ubuntu.com
*.google.com
*.android.com
*.gnome.org;
location / {
proxy_pass http://pxportal_service:8889/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-Ip $remote_addr;
proxy_buffering off;
}
}
server {
server_name portal.eca.aero;
root /data/webapp/portal;
}
PXPortal - Portal Service
- is a server HTTP based on NodeJs and ExpressJs
- simulates captive portal APIs
- saves validated mac addresses on /validate call. It's saved in memory that means, it is cleared on a service restart
- performs an ARP command to find mac address from IP client
\clearpage
Deployment
PXPortal can be deployed with a docker-compose.
Before continuing, be sure docker and docker-compose are installed on your machine.
First Run
### Clone ECA-captive repository
git clone ssh://gitolite@git.pxcom.aero:2221/ife/ECA-captive.git
This repository contains:
- docker-compose.yml: docker config of three PXPortal services
- conf: dnsmasq and Nginx configuration
- webapp: sources of portal webpage
- setup.sh: script to setup PXPortal
@startsalt
{
{T
+ECA-captive/
++ conf
+++ conf.d
++++ portal.conf
+++ dnsmasq.conf
+++ nginx.conf
++ docker-compose.yml
++ webapp
++ setup.sh
}
}
@endsalt
### 2. Running PXPortal for the first time
# Go into ECA-captive folder
cd ECA-captive
# Start all services in daemon mode
./setup.sh
### 3. Update PXPortal
(if updates are available)
# Go into ECA-captive folder
cd ECA-captive
# Pull latest updated dockers
docker-compose pull
# Restart dockers
docker-compose up -d
\clearpage
startup.sh
startup.sh allows to:
- start PXPortal and perform some sanity checks
- setup ssh config and update environment varianles used by docker-compose.yml file in order to execute arp commands from docker to host. (Required by portal_service to get MAC addresses from IP clients)
- check portal APIs are alive
\clearpage
#/bin/sh
check_ping () {
echo "[-] ping $1"
echo $1 | xargs ping -c 1 > /dev/null
if [ "$?" -ne "0" ]
then
exit
fi
}
check_wget () {
echo "[-] wget $1"
echo $1 | xargs wget -q -O out > /dev/null
if [ "$?" -ne "0" ]
then
exit
fi
}
check_docker () {
local IS_RUN=$(docker ps | grep $1 | wc -l | xargs echo -n)
if [ "$IS_RUN" -ne "1" ]
then
echo "/!\ Docker $1 is not running"
echo " Run following command for more details"
echo " docker-compose up"
exit
fi
}
faildMsg () {
if [ "$1" -ne "0" ]
then
echo "---"
echo "/!\ Setup Failed"
echo " $2"
exit
fi
}
getGateway () {
local NETWORK_MODE=`docker inspect -f "{{ .HostConfig.NetworkMode }}" $1`
docker inspect -f "{{ .NetworkSettings.Networks.$NETWORK_MODE.Gateway }}" $1
}
echo "[>] Starting PXPortal"
docker-compose up -d
sleep 1
check_docker pxportal_nginx
check_docker pxportal_dnsmasq
check_docker pxportal_service
echo "Gateway pxportal_service: $(getGateway pxportal_service)"
echo "Gateway pxportal_dnsmasq: $(getGateway pxportal_dnsmasq)"
echo "Gateway pxportal_nginx : $(getGateway pxportal_nginx)"
echo "[>] Checking ssh keys"
docker exec pxportal_service cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub > /dev/null
if [ "$?" -ne "0" ]
then
echo "[>] generating ssh keys"
docker exec pxportal_service ssh-keygen -N "" -f /root/.ssh/id_rsa
fi
SSH_PUB=$(docker exec pxportal_service cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub)
HAS_SSH=$(cat ~/.ssh/authorized_keys | grep "$SSH_PUB" | wc -l | xargs echo -n)
if [ "$HAS_SSH" -eq "0" ]
then
echo "[>] Copying public key into host authorized_keys"
echo $SSH_PUB >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
fi
echo "[>] Try ARP command from docker"
GATEWAY=$(getGateway pxportal_service)
ARP_CMD_OPT='"StrictHostKeyChecking no"'
ARP_CMD="ssh -o $ARP_CMD_OPT $USER@$GATEWAY arp -n"
echo $ARP_CMD | xargs docker exec pxportal_service
faildMsg $? "Failed to exec arp command from docker | check ssh config"
echo "[>] Updating .env"
echo "# Updated at $(date)" > .env
echo "ARP_CMD=$ARP_CMD" >> .env
echo "[>] Restarting PXPortal"
docker-compose up -d
mkdir -p /tmp/pxportal-tst
cd /tmp/pxportal-tst
echo "[>] Checking all"
check_ping "google.com"
check_ping "apple.com"
check_ping "portal.eca.aero"
check_ping "captive.eca.aero"
check_wget "test.google.com"
check_wget "test.google.com/validate"
echo "---"
echo "[!] Setup done with success"
\clearpage
## Primary Nginx Config
The ECA-portal Nginx is configured as a slave reverse proxy. That's why it is not used the 80 by default.
But to be able to handle captive portal API, the primary nginx running on port 80 should redirect all unknown URLS to portal nginx. This is an example of configuration to add into a primary nginx configuration:
....
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name _;
location / {
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Host $remote_addr;
proxy_pass http://172.19.0.1:8031;
}
access_log captive-pxportal-access.log;
error_log captive-pxportal-error.log;
}
....
\clearpage
## docker-compose.yml
version: '2'
services:
nginx:
image: nginx:alpine
container_name: pxportal_nginx
networks:
- pxportal
ports:
- "8031:80"
volumes:
- ./webapp:/data/webapp
- ./conf/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- ./conf/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d/
dnsmasq:
image: andyshinn/dnsmasq
container_name: pxportal_dnsmasq
ports:
- "53:53/tcp"
- "53:53/udp"
cap_add:
- NET_ADMIN
volumes:
- ./conf/dnsmasq.conf:/etc/dnsmasq.conf
depends_on:
- pxportal
pxportal:
container_name: pxportal_service
image: registry.preprod.pxcom.aero/pxcom-servers/pxportal-srv:latest
volumes:
- ./webapp:/usr/app/webapp
- ssh:/root/.ssh
networks:
- pxportal
environment:
- REDIRECT_TO=http://portal.eca.aero/index.html
- ARP_CMD=${ARP_CMD}
ports:
- "8889:8889"
volumes:
ssh:
networks:
pxportal:
driver: bridge
\clearpage
## Cisco configuration
Wlan
Wlan - Home
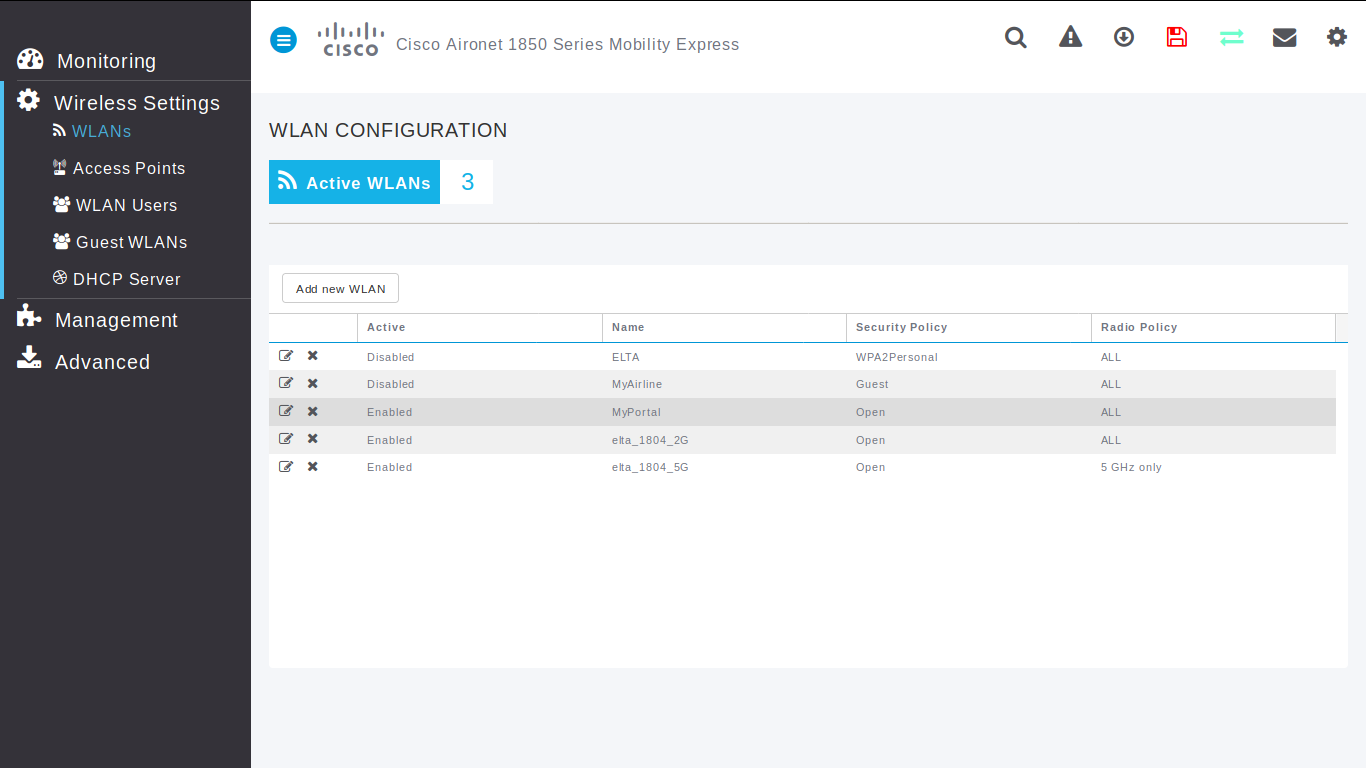
Go to Wireless Settings / WLANs page to create or configure a WLAN for passengers.
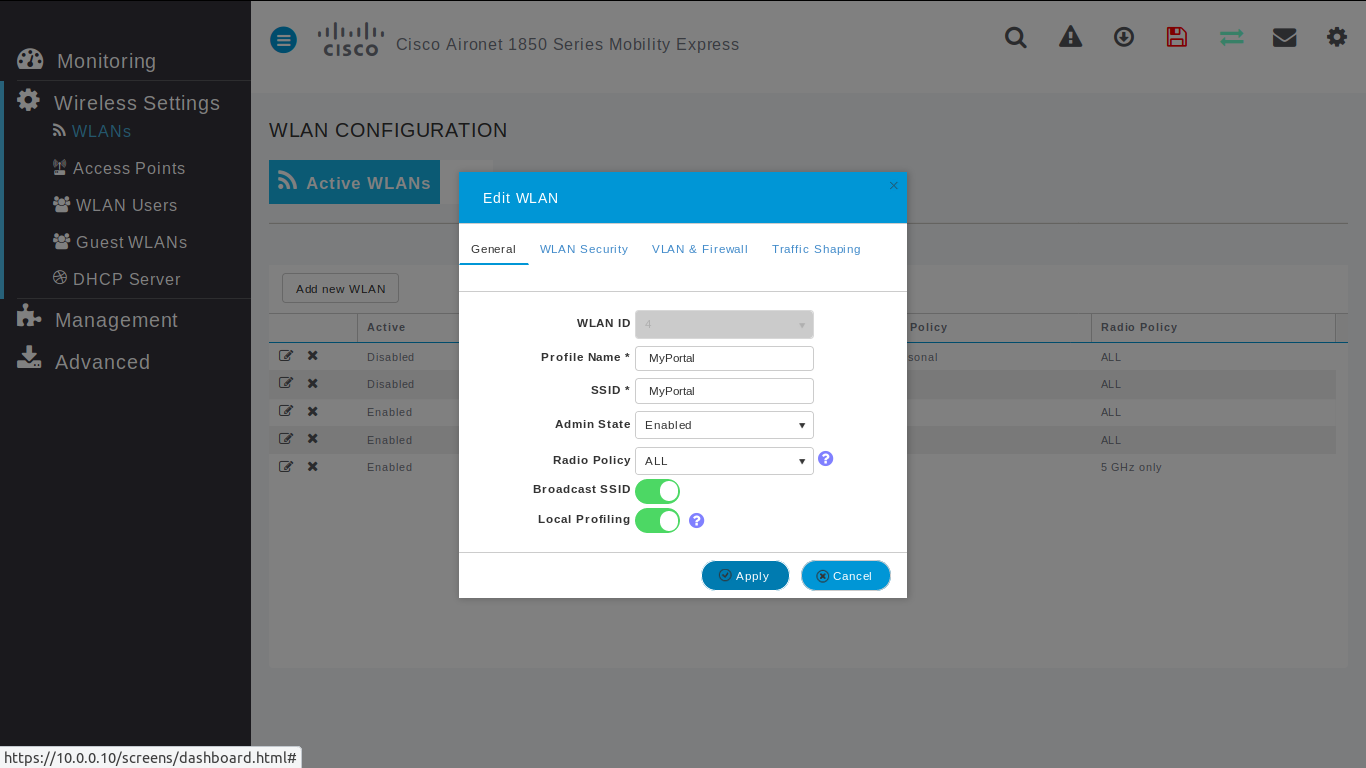
Wlan - General
- Profile Name: [Name of passengers WIFI]
- SSID: [Name of passengers WIFI]
\clearpage
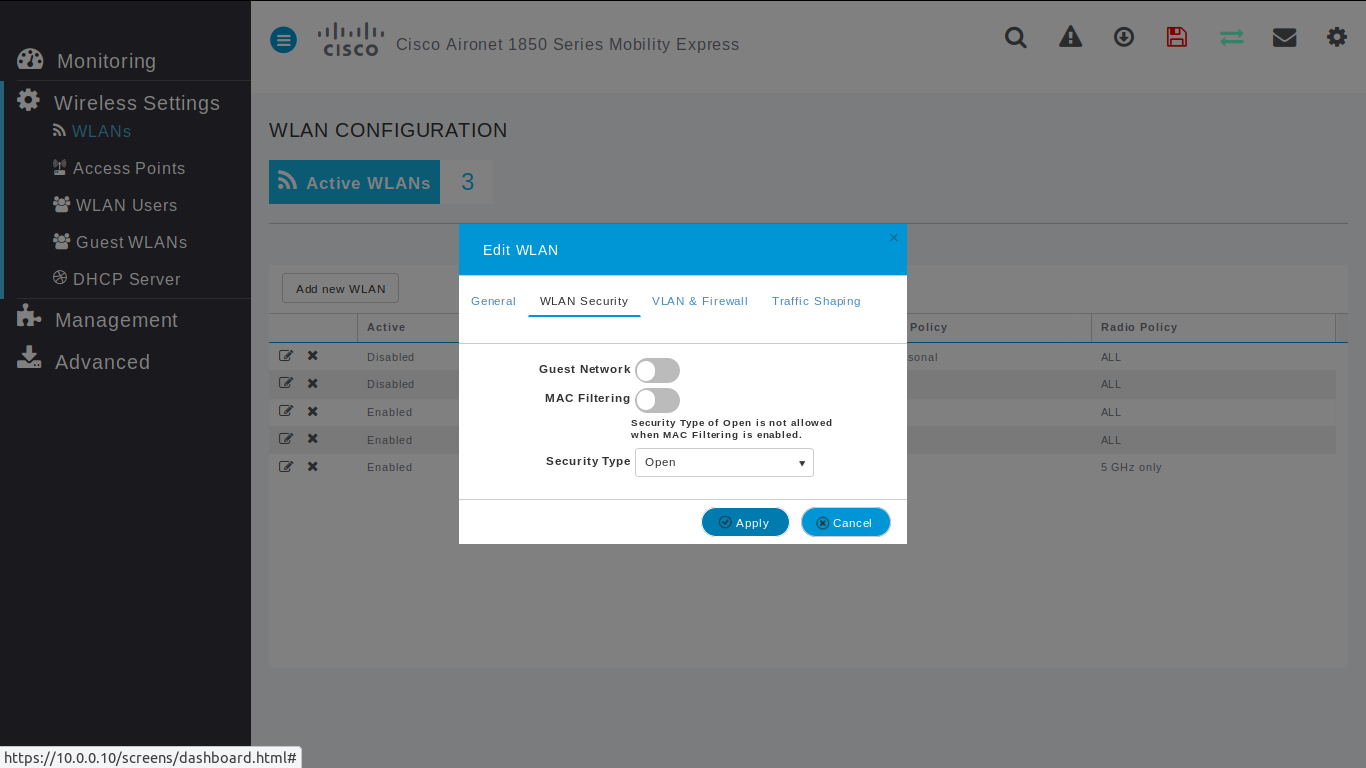
Wlan - WLAN Security
Such as CISCO captive portal forces a HTTPS page and requires to check SSL certificates from external network, PXPortal doesn't use it and provides its own captive portal. That's why Guest Network is disabled and the WIFI network is opened.
- Guest Network: disabled
- Security type: Open
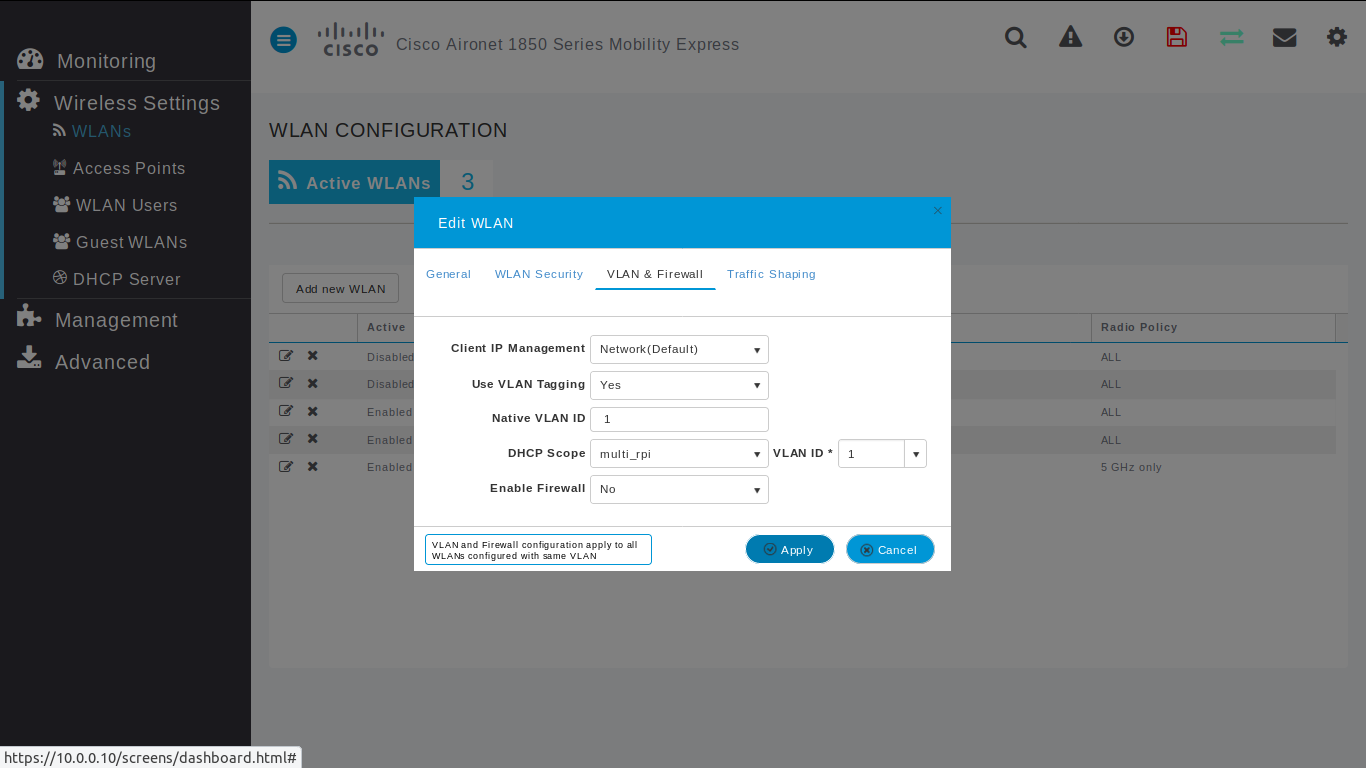
Wlan - VLAN & Firwall
Default configuration
\clearpage
Wlan - Traffic Shaping
Default configuration
\clearpage
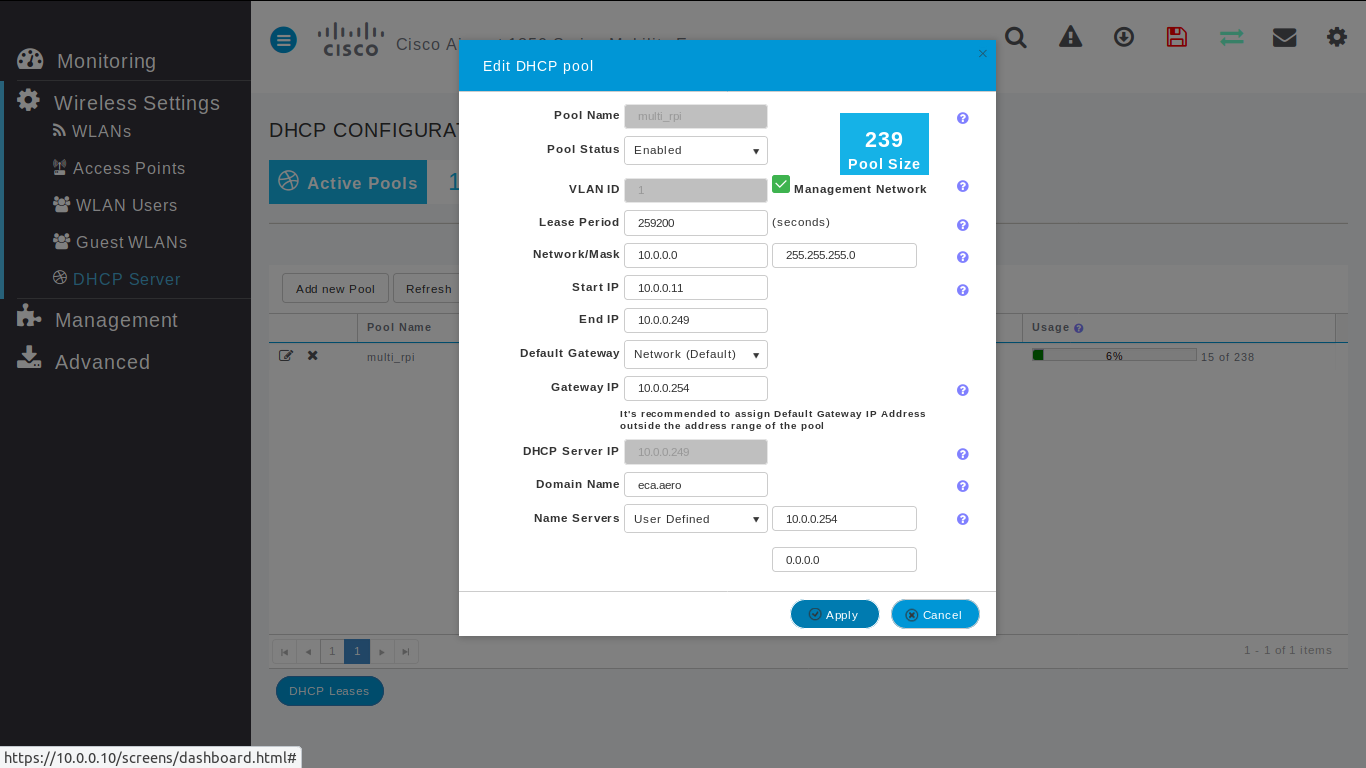
DHCP
By default, PXPortal uses Cisco DHCP.
### General
- Pool Status: Enabled
- Network / Mask: 10.0.0.0 / 255.255.255.0
- Start IP: 10.0.0.11
- End IP: 10.0.0.249
- Gateway IP: 10.0.0.254
- Domain Name: eca.aero
- Name servers: User Defined / 10.0.0.254